By
Patricia M. Dowling, DVM, MSc, DACVIM, DACVCP, Professor, Veterinary
Clinical Pharmacology, Western College of Veterinary Medicine, University of
Saskatchewan
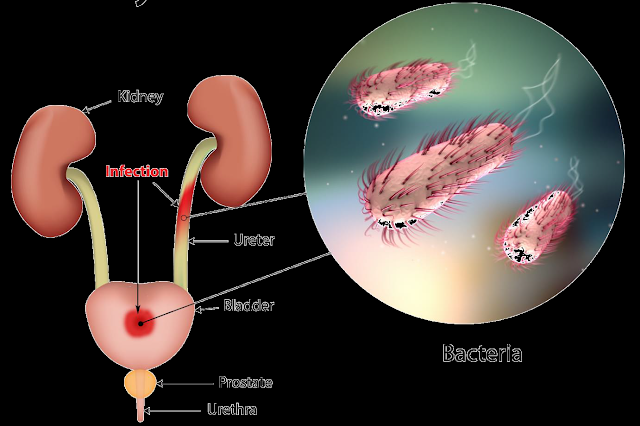
Bacterial
urinary tract infections (UTIs) typically result from normal skin and GI tract
flora ascending the urinary tract and overcoming the normal urinary tract
defenses that prevent colonization. Bacterial UTI is the most common
infectious disease of dogs, affecting 14% of all dogs during their
lifetime. Although UTIs are uncommon in young cats, the incidence of UTI is
much higher in older cats, which may be more susceptible to infection because
of diminished host defenses secondary to aging or concomitant disease (such as
diabetes mellitus, renal failure, or hyperthyroidism). Approximately two-thirds
of those cats also have some degree of renal failure. Bacterial UTIs in
ruminants are associated with catheterization or parturition in females and as
both a cause and consequence of urolithiasis in males. In horses, UTIs are
uncommon and typically associated with bladder paralysis, urolithiasis, or
urethral damage.
عادة ما تحدث الإصابات الجرثومية
للسبيل البولي (UTIs) بسبب انتقال الفلورا الطبيعية للجلد أو
السبيل الهضمي إلى السبيل البولي وتغلبها على دفاعاته الطبيعية التي تقيه من تشكل
المستعمرات. تعتبر الاصابات البولية الأكثر الأمراض المعدية شيوعاً عند الكلاب إذا
تشكل 14% من مجموع الأمراض التي تتعرض لها الكلاب طيلة حياتها. أما القطط فبالرغم
من ندرة الاصابة بالالتهابات البولية الجرثومية فإن القطط الأكبر عمراً تكون أكثر
عرضة لهذه الاصابات بسبب تضاؤل الدفاعات الناجمة عن الأمراض المتعلقة بالتقدم
بالعمر (كالسكري والفشل الكلوي أو فرط نشاط الدرق). حيث أن ثلثي هذه القطط تقريباً
تكون مصابة ببعض درجات الفشل الكلوي. أما بالنسبة للمجترات فإن الإصابات الجرثومية
للسبيل البولي تكون ناجمة عن عمليات القثطرة أو الولادات عند الإناث وأيضاً عند
الذكور تكون كنتائج مرافقة للتحصي البولي. أما الخيول فالتهاب المجاري البولية
يكون غير شائع ويترافق بشكل نمطي مع شلل المثانة والحصيات البولية أو تلف الإحليل.
Unlike
human patients, veterinary patients are often asymptomatic, and the UTI may be
an incidental finding. The consequences of untreated UTI include lower urinary
tract dysfunction, urolithiasis, prostatitis, infertility, septicemia, and
pyelonephritis with scarring and eventual kidney failure. Coagulase-positive
staphylococci are involved in the formation of struvite (MgNH4PO4)
calculi in dogs. In intact male dogs, UTI frequently extends to the prostate
gland. Because of the blood-prostate barrier, it is difficult to eradicate
bacteria from the prostate, and the urinary tract may be reinfected after
appropriate treatment, causing a systemic bacteremia, infecting the rest of the
reproductive tract, or causing an abscess within the prostate.
وبعكس مرضى البشر فإن الحيوانات
المصابة بالالتهابات البولية لا يتشكل عندها أعراض سريرية واضحة وعلى الغالب يكون
اكتشاف الإصابة على سبيل الصدفة. تتجلى عواقب الإصابة بالتهاب السبيل البولي بتعطل
المجاري البولية السفلية، التحصي، التهاب البروستات، العقم، التسمم الدموي،
والتهاب الكلية والحويضة المترافق مع التندب وبالتالي يفضي إلى الفشل الكلوي. في
حال الاختبار الإيجابي للخميرة المخثرة لجراثيم المكورات العنقودية فإننا نشاهد
ترسبات من الستروفيت (فوسفات المغنيزيوم والأمونيوم) على شكل حصوات عند الكلاب.
يمتد التهاب المجاري البولية عند ذكور الكلاب السليمة عادة إلى غدة البروستات.
وبسبب الحاجز بروستات الدموي فإن من الصعب القضاء على الجراثيم المتواجدة فيها،
وقد تعود الإصابة البولية ثانية بالرغم من العلاج الفعال لهذه الحالة الأمر الذي
يؤدي إلى التجرثم الدموي الجهازي الذي يمتد ليصيب كامل الجهاز التناسلي أو قد يسبب
خراجات داخل البروستات.
Large,
retrospective studies have documented the most common species of uropathogens
in dogs and cats, with Escherichia coli being the single most common
pathogen in both acute and recurrent UTIs. The other common pathogens include Staphylococcus,
Proteus, Streptococcus, Klebsiella, and Pseudomonas spp.
In UTIs in horses, E coli, Streptococcus, and Enterococcus
spp predominate, whereas Corynebacterium renale and E coli are
the most common pathogens in ruminants. In immunocompromised animals, funguria
from Candida spp may occur.
وثقت العديد
من الأبحاث السابقة أن الأنماط الجرثومية المألوفة التي تسبب الالتهابات البولية
عند الكلاب والقطط هي الاشريشيا كولاي (العامل الوحيد الأكثر شيوعا سواء بالإصابات
الحادة أو المتكررة)، والأنواع الأخرى المألوفة أيضاً تتضمن أجناس المكورات العنقودية،
البروتيوس، المكورات العقدية، الكليبسيلا والزوائف. بالنسبة للخيول فإن الالتهابات
البولية تكون بسبب أجناس الإي كولاي، المكورات العقدية، والمكورات المعوية هي
السائدة بينما في المجترات فإن الوتديات البولية والإي كولاي تكون هي الكائنات
الممرضة الأكثر شيوعاً. بالنسبة للحيوانات ذات المناعة المعطلة فقد تظهر حالات
الإصابة الفطرية المتسببة عن جنس المبيضات.
Antimicrobials
are the cornerstone of UTI therapy, and many animals with recurring UTIs are
managed empirically with repeated courses (see Table: Drugs Commonly Used to Treat Urinary Tract
Infections in Small Animals). This
approach fails if the underlying pathophysiology predisposing the animal to the
UTI is not addressed; as well, it encourages emergence of resistant bacteria.
With chronic UTI from highly resistant bacteria, therapeutic options are
extremely limited.
تمثل المضادات الحيوية حجر الأساس في علاج
الالتهابات البولية، وقد تم التحكم تجريبياً بالحيوانات المصابة بالتهابات بولية
بإعطائها دورات علاجية متكررة (انظر الجدول). قد يفشل هذا النهج عند حيوان معين في
حال وجود عوامل كامنة ممرضة بالتهاب المجاري البولية ذات فيزيولوجية إمراضية غير
محددة، وهذا ما يحفز ظهور مقاومة العترات الجرثومية. وفي حال الإصابات البولية
المزمنة بالجراثيم المقاومة فإن الخيارات العلاجية تكون محدودة جداً.
Drugs Commonly Used to Treat Urinary Tract Infections in
Small Animals
العقارات
المستخدمة عادة في علاج إصابات الجهاز البولي عند الحيوانات الصغيرة:
|
Drug
العقار
|
Suggested
Dosage
الجرعة المقترحة
|
Typical
Antimicrobial Activity
الاثر النمطي للمضاد الحيوي
|
|
Amoxicillinالأموكسيسليين
|
11
mg/kg, PO, bid-tid
11مغ /كغ فمويا مرتين أو
ثلاث مرات يوميا
|
Staphylococci,
streptococci, enterococci, Proteus, some E coli
يؤثر على
المكورات العنقودية والقعدية والمكورات المعوية والبروتيوس وبعض الاي كولاي
|
|
Ampicillin
الامبيسللين
|
25
mg/kg, PO, tid
25 مغ/ كغ فمويا ثلاث مرات يوميا.
|
Staphylococci,
streptococci, enterococci, Proteus, some E coli
المكورات العنقودية والعقدية
والمعوية والبروتيوس وبعض الاي كولاي
|
|
Amoxicillin-clavulanic
acid
أموكسيسلين مع حمض كلافولينيك
|
25
mg/kg, PO, tid
25مغ/ كغ فمويا ثلاث مرات يوميا
|
Staphylococci,
streptococci, enterococci, Proteus, some E coli
المكورات العنقودية والعقدية
والمعوية والبروتيوس وبعض الاي كولاي
|
|
Cephalexin/cefadroxil
سيفاليكسين وسيفادروكسيل
|
20–30
mg/kg, PO, bid-tid
20/30 مغ/كغ فمويا مرتين أو ثلاث
مرا يوميا
|
Staphylococci,
streptococci, Proteus, E coli, Klebsiella
المكورات العنقودية والعقدية
البروتيوس والاي كولاي والكليبسيلا.
|
|
Cefovecin
سيفوفيسين
|
8
mg/kg, SC, every 14 days
8 مغ/كغ تحت الجلد كل 14 يوم
|
Proteus, E coli
البروتيوس والاي كولاي
|
|
Cefpodoxime
سيفوبودوكسيم
|
5–10
mg/kg/day, PO
5-10 مغ/كغ/يوم فمويا
|
Proteus, E coli
بروتيوس وإي كولاي
|
|
Ceftiofur
سيفتيوفور
|
2
mg/kg/day, SC
2مغ/كغ /يوم تحت الجلد
|
Proteus, E coli
بروتيوس وإي كولاي
|
|
Choramphenicol
كلورامفينيكول
|
Dogs:
25–50 mg/kg, PO, bid-tid
الكلاب: 25-50 مغ/كغ، فمويان مرتين
أو ثلاث مرات يوميا
Cats:
50 mg/kg, PO, bid
قططك: 50مغ/كغن فمويا، يوميا
|
Staphylococci,
streptococci, enterococci, E coli
مكورات عنقودية وعقدية ومعويات وإي
كولاي
|
|
Doxycycline
دوكسيسيكلين
|
5
mg/kg, PO, bid
5مغ/ كغ فمويا مرتين يوميا.
|
Streptococci,
some activity against E coli, staphylococci, and enterococci at high
urine concentrations
مكورات عنقودية وفعالية جزئية على
الاي كولاي والقعديات والمعويات في التراكيز العالية في البول.
|
|
Enrofloxacin,
orbifloxacin, marbofloxacin, pradofloxacin (cats only)
إنروفلوكساسين أوربيفلوكساسين
ماربوفلوكساسين برادوفلوكساسين (قطط فقط)
|
2.5–10
mg/kg/day, PO
2.5-10مغ/كغ /يوم فمويا
|
Staphylococci,
E coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Enterobacter
المكورات العنقودية والاي كولاي
والبروتيوس والكليبسيلا والزوائف والجراثيم المعوية
|
|
Gentamicin
جنتاميسين
|
4–6
mg/kg/day, SC
4-6مغ/كغ/يوم تحت الجلد
|
Staphylococci,
some streptococci, some enterococci, E coli, Proteus, Klebsiella,
Pseudomonas, Enterobacter
المكورات العنقودية وبعض العقديات
والمعويات والاي كولاي والبروتيوس كليبسيلا وبسيدوموناس والبكتريا المعوية.
|
|
Nitrofurantoin
نيتروفيوران
|
5
mg/kg, PO, tid
5مغ/كغ فمويا مرتين يوميا.
|
Staphylococci,
some streptococci, enterococci, E coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
المكورات العنقودية وبعض العقديات
والمكورات المعوية الاي كولاي الكليبسيلا والبكتريا المعوية
|
|
Tetracycline
تيتراسيكلين
|
18
mg/kg, PO, tid
18 مغ/ كغ فمويا ثلاث مرات في اليوم
|
Streptococci,
some activity against E coli, staphylococci, and enterococci at high
urine concentrations
المكورات العنقودية وبعض الفعالية ضد
الاي كولاي المكورات العقدية والالمكورات المعوية في التراكيز العلية في البول
|
|
Trimethoprim-sulfa
السلفا مع التريمثوبريم
|
15
mg/kg, PO, bid
15 مغ/كغ فمويا مرتين يوميا
|
Streptococci,
staphylococci, E coli, Proteus, some activity against Klebsiella
المكورات العنقودية والعقدية والاي
كولاي وبعض الفعالية ضد الكليبسيلا
|
Antimicrobial Therapy:
العلاج
المضاد الجرثومي:
Urine
culture is the “gold standard” for diagnosis of UTI. Indications to perform
urine culture include visualization of bacteria during urine sediment
examination, evidence of pyuria, dilute urine (<1.013 SG),
immunosuppression, and diabetes mellitus or hyperadrenocorticism. Antimicrobial
susceptibility testing should be done with complicated or recurrent cases of
UTIs, immunosuppressed animals, animals recently catheterized, or animals
treated with antimicrobials within the preceding 3 wk (because of selection for
antimicrobial resistance). In addition, culture and susceptibility testing
should be performed in cases that do not respond within 7 days of therapy for
UTI or in cases associated with multiple pathogens.
المعيار الذهبي لتشخيص التهابات
السبيل البولي هو زرع البول مخبرياً. تتضمن إجراءات الزرع الجرثومي للبول مشاهدة
البكتريا بعمل مسحات الفحص المجهري، دلائل على وجود الفطور، تمديد البول
(<1.013 SG)، الكبح
المناعي، والداء السكري أو فرط إفراز الهرمونات القشرية، ويجب إجراء اختبار الحساسية
الجرثومية في حال الحالات المعقدة أو المتكررة عند الحيوانات ذات المناعة
المكبوحة، الحيوانات التي أجري عليها عملية قثطرة بولية، والحيوانات المعالجة بالمضادات
الحيوية التي تتجاوز 3 أسابيع (بسبب المقاومة الانتقائية للمضادات الجرثومية). إضافة
إلى ما سبق فإن الزرع البولي واختبار الحساسية يجب أن يجريان في حالة عدم
الاستجابة للعلاج خلال 7 أيام بعد الإصابة بالالتهاب البولي أو في الحالات
المرتبطة بالإصابات متعددة المسببات الممرضة.
High
urine concentrations of antimicrobials are correlated with efficacy in
treatment of uncomplicated cystitis. But in complicated cases and in
pyelonephritis, tissue concentrations may be equally important. Most
antimicrobials undergo renal elimination to a great extent, so urine
concentrations may be up to 100 times peak plasma concentrations. Drug
excretion through the kidney involves various processes such as secretion
and/or reabsorption in different parts of the nephron, depending on the
molecular structure of the drug, its pKa, the pH in the tubular
fluid, and degree of protein binding. The flow of urine through the urinary
tract is part of the defense against invading pathogens, because the flow of
fluid rinses the epithelial linings. High urine antimicrobial concentrations
are important for eradication of bacteria in the urine, but for infection of
the bladder wall or renal tissue it is necessary to use antimicrobials that
have active concentrations in the tissues. Serum or plasma concentrations are
useful surrogate markers for antimicrobial concentrations in the renal or
bladder tissues.
ترتبط التراكيز
العالية للمضادات الحيوية في البول مع فعالية علاج التهاب المثانة غير المعقد. أما
في حال التعقد أو الإصابة بالتهاب الكلية والحويضة فمن الضروري أن يكون التركيز
متوافراً في الأنسجة بقدر مماثل للبول. معظم المضادات الحيوية تطرح عن طريق البول
بنسب عالية لذلك يكون تركيزها في البول أكثر بمئة مرة من تركيزها في البلازما.
يعتمد إطراح الدواء عن طريق الكلى على العديد من الآليات كآلية الإفراز وإعادة الامتصاص
في مختلف أجزاء النيفرون بالاعتماد على التركيب الجزيئي للعقار، والتركيز الحمضي
في السائل الأنبوبي، ونسبة ارتباطه مع البروتين. يعد جريان البول في السبيل البولي
أحد عوامل خطوط الدفاع ضد عوامل إمراضية معينة، لأن جريانه يعمل على شطف الطبقة
الظهارية. فالتراكيز العالية للمضادات الجرثومية في البول أمر مهم للقضاء على
البكتريا في البول، ولكن من المهم أيضاً في حال إصابة جدار المثانة أو الأنسجة
البولية أن نستخدم مضادات حيوية ذات تراكيز فعالة في هذه الأنسجة. يفيد قياس تركيز
المضاد الحيوي في المصل أو في الدم كبديل لمعرفة تركيزه في الأنسجة البولية أو
المثانة.
In
addition to having the appropriate antimicrobial activity and achieving
effective concentrations in urine, the selected antimicrobial should be easy
for owners to administer, have few adverse effects, and be relatively inexpensive.
Once urine culture and sensitivity results are known, the bacterial minimum
inhibitory concentration (MIC) can be compared with the mean urinary
concentration of the drug and an appropriate antimicrobial chosen.
يجب بالإضافة إلى الحرص على فعالية
المضاد الحيوي وتركيزه الملائمين في البول أن نحرص على كون إعطائه للحيوان سهلاً وأن
يكون له أعراض جانبية قليلة وغير مكلف مادياً. فبمجرد معرفة المضاد المناسب بعد
زراعة البول واختبار الحساسية يمكن إجراء اختبار التركيز الأدنى الكابح للجراثيم (MIC) لحساب معدل تركيزه في البول وملاءمته
للعلاج.
Amoxicillin and ampicillin are bactericidal and relatively
nontoxic, with a spectrum of antibacterial activity greater than that of
penicillin G. They have excellent activity against staphylococci, streptococci,
enterococci, and Proteus, and may achieve urinary concentrations high
enough to be effective against E coli and Klebsiella. Pseudomonas
and Enterobacter are resistant. Amoxicillin is more bioavailable in dogs
and cats (better absorbed from the GI tract) than ampicillin, hence the lower
dosage. Absorption of ampicillin is also affected by feeding, so therapeutic
success may be easier to achieve with amoxicillin. As penicillins, they are
weak acids with a low volume of distribution, so they do not achieve
therapeutic concentrations in prostatic fluid.
الأمبيسلين والأموكسيسلين: هما مضادان
حيويان قاتلان للجراثيم وغير سامين نسبياً، ويمتلكان طيفاً جرثومياً يفوق البنسلين
ج. ولهما فعالية ممتازة على المكورات العنقودية والعقدية والمعوية والبروتيوس وقد
يحققان تركيزاً في البول يكفي للتأثير على الإي كولاي والكليبسيلا. أما الزوائف
والجراثيم المعوية (الأمعائيات) فهي مقاومة لهما. يكون توافر الأموكسيسلين عند
الكلاب والقطط (أفضل امتصاصاً من الأمعاء) أكثر من الأمبيسليين فبالتالي تكون
جرعته أقل. ويتأثر امتصاص الأمبيسلين أيضاً بالغذاء (وجود الطعام بالمعدة) لذلك
فقد يكون تحقيق علاج ناجح في حال الأموكسيسلين. وكما البنسلينات فهي حموض ضعيفة مع
أحجام توزع منخفضة، لذلك فهي لا تحقق تراكيز علاجية في سوائل البروستات.
Amoxicillin-clavulanic
acid has an increased spectrum of
activity against gram-negative bacteria because of the presence of clavulanic
acid. Clavulanic acid irreversibly binds to β-lactamases, allowing the
amoxicillin fraction to interact with the bacterial pathogen. This combination
usually has excellent bactericidal activity against β-lactamase–producing
staphylococci, E coli, and Klebsiella. Pseudomonas and Enterobacter
remain resistant. However, clavulanic acid undergoes some hepatic metabolism
and excretion, so much of the antimicrobial activity in the bladder may be due
to the high concentrations of amoxicillin achieved in urine. Thus, despite an
unfavorable susceptibility report for amoxicillin, clinically amoxicillin alone
may be as effective as amoxicillin-clavulanic acid to treat UTIs.
الأموكسيسلين مع حمض الكلافولانيك: يمتلكان
طيف فعالية موسعة على الجراثيم سالبة الغرام بسبب وجود حمض الكلافولانيك فهو يرتبط
بشكل غير عكوس مع البيتالاكتاماز مانحاً جذر الأموكسيسلين فسحة للتعامل مع
الجراثيم الممرضة. وهذه التركيبة لها تأثير ممتاز على جراثيم المكورات العنقودية
المفرزة لخميرة البيتالاكتاماز والاي كولاي والكليبسيلا. ولكن لا تزال الزوائف
والأمعائيات مقاومة لها. مع العلم أن حمض الكلافولانيك يخضع لبعض الاستقلابات
والإفرازات الكبدية والفعالية المضادة للجراثيم له في المثانة تكون بسبب التركيز
العالي للأموكسسلين المحقق في البول. وهكذا وبالرغم من تقارير الحساسية غير
المرغوبة للأموكسيسلين، فإن له وحده دون اقترانه مع الكلافولانيك التأثير ذاته على
التهاب المجاري البولية.
Cefadroxil and cephalexin are first-generation cephalosporins.
Cefadroxil is a veterinary-labeled suspension product, whereas cephalexin is
available in both human and veterinary formulations as tablets, paste, or
suspension products. Like the penicillins, they are bactericidal, acidic drugs
with a low volume of distribution and are relatively nontoxic. Vomiting and
other GI signs may occur in dogs and cats treated with cephalosporins.
Cephalosporins have greater stability to β-lactamases than penicillins, so they
have greater activity against staphylococci and gram-negative bacteria. They
have excellent activity against Staphylococcus spp, Streptococcus
spp, E coli, Proteus, and Klebsiella. Pseudomonas,
enterococci, and Enterobacter are resistant.
سيفادروكسيل والسيفاليكسين: وهما
الجيل الأول من السيفالوسبورينات، يبقى السيفادروكسيل معلقاً بيطرياً بامتياز
بينما يستعمل السيفالكسين في كل من البشر والحيوانات على شكل مضغوطات أو مراهم أو
معلقات. وهي قاتلة للجراثيم كما البنسلينات وهي مركبات حمضية مع حجم توزع منخفض
وغير سامة نسبياً. قد يحدث التقيؤ والأعراض المعدية المعوية الأخرى عند الكلاب
والقطط بعد تناول السيفالوسبورينات. لهذه المركبات ثباتية عند تأثرها بأنزيمات
البيتالاكتاماز أكثر من البنسلينات لذا فلها تأثير أكبر ضد المكورات العنقودية
والجراثيم سلبية الغرام. ولهما تأثيراً ممتازاً ضد جنس المكورات العنقودية، جنس
المكورات العقدية، الإي كولاي، البروتيوس، البروتيوس، والكليبسيلا. أما الزوائف
والمكورات المعوية والامعائيات كلها مقاومة.
Cefovecin is an injectable, third-generation cephalosporin approved
for treatment of dogs with a UTI due to E coli or Proteus.
In cats, it is only approved for skin infections but may be used in an
extra-label manner for UTIs. With SC dosing, therapeutic concentrations are
achieved for 14 days, making this an attractive treatment choice for fractious
animals.
سيفوسين: هو الجيل الثالث من
السيفالوسبورينات القابلة للحقن أثبتت فعالية في علاج الكلاب المصابة بالتهاب
المجاري البولية بتأثير الاي كولاي أو البروتيوس. أما في القطط فلا يكون فعالاً
إلا في علاج الالتهابات الجلدية ولكنه قد يستخدم كعلاج للمجاري البولة ولكن خارج
مجال استطباباته المثبتة. يتم تحقيق التركيز العلاجي في حال الحقن تحت الجلدي خلال
14 يوماً الأمر الذي يجعله علاجاً ملائماً للحيوانات المكسورة.
Cefpodoxime is an oral, third-generation cephalosporin approved for use
in dogs for skin infections (wounds and abscesses), but it is used extra-label
for treatment of canine UTI. Cefpodoxime has a relatively long half-life in
dogs, so it is dosed once daily.
سيفبودوكسيم: هو مضاد حيوي فموي ينتمي
للجيل الثالث من السيفالوسبورينات أثبت فعالته لعلاج إلتهابات الجلد عند الكلاب
(الجروح والخراجات) ولكنه يستعمل - كاستطباب غير مثبت - لعلاج التهابات المجاري
البولية الكلبي. ويمتلك السيفودوكسيم نصف عمر طويل نسبياً عند الكلاب، لذلك يعطى
مرةً واحدةً يومياً.
Ceftiofur is an injectable cephalosporin approved for respiratory
disease in horses, swine, and cattle and for treatment of canine UTI caused by E
coli and Proteus. Ceftiofur has pharmacokinetic properties very
different from those of other cephalosporins. After injection, ceftiofur is
immediately metabolized to desfuroylceftiofur, which has different
antimicrobial activity than the parent compound. Desfuroylceftiofur has
equivalent activity to ceftiofur against E coli (MIC 4 mcg/mL) but is
much less active against Staphylococcus spp and has variable activity
against Proteus (MIC 0.5–16 mcg/mL). Because of the instability of
desfuroylceftiofur, microbiology services use a ceftiofur disk when performing
susceptibility testing, so a false expectation of therapeutic efficacy may
result for some pathogens. Pseudomonas, enterococci, and Enterobacter
spp are resistant to ceftiofur and desfuroylceftiofur. Ceftiofur is associated
with a duration- and dose-related thrombocytopenia and anemia in dogs, which
would not be expected with the recommended dosage regimen.
السيفتيوفور: هو مضاد حيوي من
السيفالوسبورينات معد للحقن أثبت فعاليته للامراض التنفسية عند الخيول، والخنازير،
والماشية وعلاج التهاب المجاري البولية عند الكلاب المتسبب عن الإي كولاي
والبروتيوس. للسيفتيوفور خواص حركية دوائية تختلف عن باقي مركبات
السيفالوسبورينات. فبعد الحقن مباشرة فإن السيفتيوفور يستقلب في الحال لمركب
ديسفورويل سيفتيوفور الذي يختلف بفعاليته المضادة للجراثيم عن المركب الناشئ عنه.
ولهذا المستقلب فعالية مماثلة للسيفتيوفور ضد الاي كولاي (تركيز الكبح الأدنى 4 مكغ/
مل) ولكنه أقل تأثيراً على جنس المكورات العنقودية بكثير، وله تأثير مغاير بالنسبة
للبروتيوس (تركيز الكبح الأدنى 0.5-16 مكغ/ مل). وبسبب عدم ثبات الخدمات الحيوية
التي يقدمها ديسفورويل سيفتيوفور لا تطابق اختبار الحساسية للسيفتوفور المجرى في
المخابر فإن التوقعات العلاجية التي قد نحصل عليها تكون مزيفة بالنسبة لبعض
المسببات المرضية، كل من جنس الزوائف والأمعائيات والمكورات المعوية تمتلك مقاومة
ضد السيفتيوفور ومستقلبه أيضا. للسيفتيوفور علاقة مع نقص الصفيحات وفقر الدم عند
الكلاب في حال تم استخدامه لفترات طويلة أو جرعات عالية، التي قد لا تكون متوقعة
ضمن الجرعة المنصوح بها.
Chloramphenicol has a high volume of distribution, and high tissue
concentrations can be achieved, including in the prostate of male dogs and
cats. It is active against a wide range of gram-positive and many gram-negative
bacteria, against which it is usually bacteriostatic. Chloramphenicol is
typically active against enterococci, staphylococci, streptococci, E coli,
Klebsiella, and Proteus. Pseudomonas are resistant. North
American isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus
pseudintermedius are typically susceptible. Well known for causing
idiosyncratic (non-dose-dependent) anemia in people and dose-dependent bone
marrow suppression in animals, its use in both human and veterinary medicine is
increasing because of resistance to other antimicrobial drugs.
الكلورامفينيكول: له حجم توزع عال في
الأنسجة بما في ذلك البروستات عند ذكور الكلاب. وهو فعال على طيف واسع من إيجابيات
الغرام والعديد من سلبيات الغرام، وهو عادة موقف لنمو الجراثيم. يستعمل
الكلورامفينيكول عادة ضد المكورات المعوية والمكورات العنقودية والاي كولاي
والكليبسيلا والبروتيوس. وتكون الزوائف مقاومة له. وقد عزل في شمال أمريكا عترات
من المكورات العنقودية أوريوس والمكورات العقدية بسيديتريميدوس المقاومة
للميثيسللين على الرغم من كونها عادة حساسة لهذا المضاد. وبالرغم من تاثيره المشهور
وغير المتعلق بالجرعة ألا وهو فقر الدم عند البشر وكبح نقي العظام المتعلق بالجرعة
عند الحيوانات فإن استعماله لدي الجنسين (البشر والحيوان) يزداد بسبب مقاومة
الجراثيم لباقي المضادات الحيوية.
Enrofloxacin,
orbifloxacin, and marbofloxacin are all
fluoroquinolones approved to treat UTIs in dogs; although all are used in cats,
only some are approved for this use. Pradofloxacin is only approved for
skin infections in cats in North America, but it is approved for treatment of
UTI in dogs in Europe and is used to treat feline UTI. The fluoroquinolones are
bactericidal, amphoteric drugs. They possess acidic and basic properties but
are very lipid soluble at physiologic pH (pH 6–8) and thus have a high volume
of distribution. All fluoroquinolones usually have excellent activity against
staphylococci and gram-negative bacteria, but they may have variable activity
against streptococci and enterococci. The therapeutic advantages of these drugs
are their gram-negative antimicrobial activity and high degree of lipid
solubility. They are the only orally administered antimicrobials effective
against Pseudomonas. Therefore, fluoroquinolones should be reserved for
UTIs that involve gram-negative bacteria, especially Pseudomonas, and
for UTIs in intact male dogs and cats because of their excellent penetration
into the prostate gland and activity in abscesses. They are
concentration-dependent killers with a long postadministration effect, so once
daily, high-dose therapy for a relatively short duration of treatment is
effective.
الانروفلوكساسين والأوربيفلوكساسين
والماربوفلوكساسين كلها من مركبات الفلورفينيكول المثبت تأثيرها على التهاب
المجاري البولية عند الكلاب، وتستعمل جميعها أيضا عند القطط ولكن بعضها فقط يؤثر
بولياً. أثبت بارادوفلوكساسين تأثيره على التهابات الجلد فقط عند القطط في شمال
امريكا ولكنه مستعمل لعلاج التهابات المجاري البولية عند الكلاب في أوروبا وهو
مستخدم لعلاج التهاب مجاري البول عند القطط أيضاً. الفلوروكينولونات هي قاتلات
للبكتريا متذبذبة. فهي تبدي خواصاً حمضية وقلوية ولكنها تختلف بانحلالها بالدسم
ضمن الحموضة البيولوجية (6-8) فهي بذلك ذات حجم توزع واسع. ولجميع مركبات
الفلوروكينولونات تأثيراً ممتازاً على العقديات والمكورات المعوية. والمزايا
العلاجية لهذه المركبات تكمن في تأثيرها على الجراثيم سالبة الغرام ونسبة انحلالها
العالية في الدسم. وهي المضادات الحيوية الوحيدة المعطاة فموياً وتؤثر على
الزوائف. لذلك فهذه الزمرة (الفلوروكينولونات) يجب أن تدخر لعلاج التهابات المجاري
البولية المتسببة عن الجراثيم سالبة الغرام وخاصة الزوائف، والتهاب المجاري
البولية عند ذكور الكلاب والقطط السليمة كونها تمتلك نفاذية ممتازة تصل إلى غدة
البروستات وفعاليتها على الخراجات. وهي مركبات قاتلة معتمدة على التراكيز وتتميز
بأنها مديدة التأثير بعد الاعطاء، لذلك فجرعة واحدة عالية يوميا لفترات قصيرة
نسبيا من العلاج تكون فعالة وكافية.
Fluoroquinolones
should be avoided for chronic, low-dose therapy, because this encourages
emergence of resistant bacteria that are cross-resistant to other antimicrobial
drugs as well. Cases that involve Pseudomonas should be carefully
investigated for underlying pathology, which must have corrected if possible.
Once Pseudomonas spp become resistant to the fluoroquinolones, there are
no other convenient therapeutic options.
يجب تجنب إعطاء الفلوروكينولونات بشكل
مديد وبجرعات منخفضة خوفاً من تحفيز إنشاء عترات جرثومية منيعة وتنتج مناعة
تصالبية مع مضادات حيوية أخرى. الحالات التي لها علاقة مع الزوائف يجب أن يتم
التحري عنها بحرص إن كانت تخضع للمسبب المرضي الذي يجب أن تصحح كلها إن أمكن ذلك.
وفي الوقت الذي تطور فيه الزوائف مقاومة للفوروكينولونات، فلن يكون هناك علاج كاف
لهذه الجراثيم بعدها.
Gentamicin and the other aminoglycosides are very large, polar
(water-soluble) molecules, so they have a low volume of distribution and do not
penetrate the blood-prostate barrier. They are not absorbed orally and must be
given by SC, IM, or IV injection. The aminoglycosides have a similar spectrum
of activity to that of the fluoroquinolones, but their use for UTI is limited
because of the necessity of parenteral injections and the risk of toxicity with
anything but short-term use. Like the fluoroquinolones, the aminoglycosides are
concentration dependent, bactericidal killers with a long post administration
effect, so once-daily therapy of short duration is effective and minimizes the
risk of nephrotoxicity. They can be considered for in-hospital or outpatient
treatment of UTI due to fluoroquinolone-resistant pathogens; however, the
importance of identifying and correcting underlying pathology must be
emphasized.
الجنتاميسين: والأمينوغليكوزيدات
الأخرى هي مجموعة كبيرة جداً (وهي جزيئات قطبية منحلة في الماء) لذلك فهي ذات حجم
توزع منخفض ولا تنفذ من حاجز الدم – بروستات. وهي غير ممتصة عند إعطائه فموياً ويجب
إعطائها بالطرق (تحت الجلد، حقن عضلي، أو حقن وريدي). للأمينوغليكوزيدات الطيف
العلاجي ذاته للفلوروكينولونات ولكن استعمالها بالنسبة لالتهابات السبيل البولي
محدودة بسب ضرورة استعماله حقنا والخطورة المتعلقة بتفاعله مع أي شيء مسبباً تسمماً
واستخدامه قصير الأمد. وكما الفلروكينولونات فإن فعالية الامينوغليكوزيدات تعتمد
على الجرعة وهي قاتلات للجراثيم مع فعالية مديدة بعد الإعطاء، لذا فيكفي إعطاؤها
مرة يومياً علاجياً ولمدة قصيرة يكون فعالاً وذو تعقيدات سمية للكبيبات الكلوية.
يمكن أن تعتبر للاستعمال في المستشفيات وضمن عيادات المرضى لعلاج التهابات السبيل البولي للمسببات المرضية
المقاومة للفلوروكينولونات، و يجب التأكيد على أهمية تحديد وتصحيح الأمراض الكامنة.
Nitrofurantoin is a human product available as tablets, capsules, and a
pediatric suspension. It is not commonly used in veterinary medicine. It is
typically used only for treatment of UTI in people, because it has a very low
volume of distribution, and therapeutic concentrations are attained only in
urine. It is considered a carcinogen, so it is banned for use in food-producing
animals, but its use in small animals is increasing with the rising rates of
antimicrobial resistance to veterinary antimicrobials. Nitrofurantoin is used
for infections caused by E coli, enterococci, staphylococci, Klebsiella
spp, and Enterobacter spp. It is increasingly indicated for treatment of
UTIs caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria, which are otherwise difficult to
treat using conventional veterinary antimicrobial agents. The pharmacokinetics
and adverse effect profile of nitrofurantoin have not been investigated in
dogs, cats, or horses, and the need for multiple daily dosing makes it
inconvenient for owners.
النتروفيوان: موجودة عند البشر على
شكل حبوب ومضغوطات ومعلقات للأطفال. فهو غير شائع الاستخدام في الحقل البيطري. وهو
عادة يستخدم عند البشر لعلاج التهاب المجاري البولية لأنه يمتلك حجم توزع ضئيل جداً
والتراكيز العلاجية تحقق فقط في البول. وهو يعتبر عقاراً مسرطناً، لذلك لا يستخدم
عند الحيوانات المأكولة ولكن استعماله يزداد اتساعاً عند الحيوانات الصغيرة
بالترافق مع تطور مقاومة المسببات المرضية لباقي المضادات الحيوية البيطرية الأخرى.
يستعمل النيتروفيوران لعلاج الإصابة بالاي كولاي والمكورات المعوية والمكورات
العنقودية وجنس الكليبسيلا وجنس الأمعائيات. وهو مستطب بشكل متزايد في حال الاصابة
بالتهاب المجاري البولية الناشئة عن المسببات المرضية المعندة على الكثير من المضادات
الحيوية. ولم يتم التحري عن الآثار الجانبية والحركية الدوائية عند الكلاب والقطط
أو الخيول بالنسبة للنيتروفيوران وحتى الجرعات اليومية المطلوبة الأمر الذي لا
يريح مالكي الحيوانات.
Tetracyclines are bacteriostatic, amphoteric drugs with a high volume of
distribution. Tetracyclines are broad-spectrum antimicrobials, but because of
plasmid-mediated resistance, susceptibility is variable in staphylococci,
enterococci, Enterobacter, E coli, Klebsiella, and Proteus.
In most tissues, Pseudomonas spp are resistant. However, the
tetracyclines are excreted unchanged in urine, so high urinary concentrations
may result in therapeutic efficacy. Doxycycline is a very lipid-soluble
tetracycline better tolerated in cats and reaches therapeutic concentrations in
the prostate, so it may be useful for some UTIs. Doxycycline may also be
effective to treat methicillin-resistant staphylococcal UTIs. If capsules are
administered, it is critical to have the animal drink afterward to ensure
passage into the stomach. If capsules remain in the esophagus, severe local
necrosis with subsequent esophageal stricture can occur.
التيتراسيكلين: هي مضادات موقفة
للجراثيم مذبذبة تمتلك حجم توزع عالٍ في الجسم. التتراسيكلينات هي مضادات حيوية
واسعة الطيف ولكن بسب مقاومة التوسط البلاسميدي فإن الحساسية متغايرة بالنسية لكل
من المكورات العنقودية والمكورات المعوية والامعائيات الاي كولاي الكليبسيلا
والبروتيوس. وتعتبر الزوائف مقاومة في معظم الانسجة، ومع ذلك فباعتبار أن
التتراسيكلينات تطرح غير بدون تغيير في البول فإن تراكيزها العالية فيه قد يكون
لها الأثر العلاجي. الدوكسيسيكلين هو من التتراسيكلينات شديدة الانحلال بالدسم
وتحمله أفضل عند القطط ويصل للتراكيز العلاجية في البروستات لذلك فقد يكون مفيداً
لعلاج التهابات المجاري البولية. وقد يكون الدوكسيسيكلين مناسباً للتأثير على
المكورات العنقودية البولية المقاومة لمضادات الميثيسلين. إن تم إعطاء الحيوان
كبسولات من العقار نفسه فيجب التأكد من شربه كميات وافرة من الماء لضمان وصول
المضغوطات للمعدة لأن بقائها في المريء قد يؤدي إلى العديد من التنكرزات الموضعية
اللاحقة في بنيته.
Trimethoprim-sulfonamides (TMP-sulfas) are combinations of two very different drugs
that act synergistically on different steps in the bacterial folic acid
pathway. Trimethoprim is a bacteriostatic, basic drug with a high volume of
distribution and a short elimination half-life, whereas the sulfonamides are
bacteriostatic, acidic drugs with a medium volume of distribution and long
half-lives (ranging from 6 to >24 hr). These drugs are formulated in a 1:5
ratio of TMP to sulfa, although the optimal bactericidal concentration is a ratio
of 1:20 TMP:sulfa. Microbiology services use the 1:20 ratio in susceptibility
testing; however, the widely varying pharmacokinetic properties of this drug
combination make it difficult to determine a therapeutic regimen that achieves
the 1:20 ratio at the infection site. Although the combination does penetrate
the blood-prostate barrier, sulfa drugs are ineffective in purulent material
because of freely available para-aminobenzoic acid from dead neutrophils. The
combination of TMP-sulfa is synergistic and bactericidal against staphylococci,
streptococci, E coli, and Proteus. Activity against enterococci
and Klebsiella is variable, and Pseudomonas is resistant.
TMP-sulfas are associated with a number of adverse effects, and chronic
low-dose therapy may result in bone marrow suppression and keratoconjunctivitis
sicca in dogs.
التريميثوبريم والسلفوناميدات: (TMP-sulfas)
هي مشاركة لعقارين مختلفين تماماً ويتآزران بأطوار مختلفة للتأثير على منحى تخليق
فوليك أسيد الجرثومي. فالتريميثوبريم هو موقف للجراثيم ولهذا العقار الأصلي حجم
توزع عالي وزمن نصف عمر إطراحه قصير. بينما السلفوناميدات هي موقفات للجراثيم
حمضية التفاعل مع حجم توزع متوسط وزمن نصف عمر طويل (يتراوح بين 6>24 ساعة).
وتجمع بنسب 1إلى 5 بالنسبة للسلفا وهو التركيز الأمثل لإيقاف الجراثيم أما الجمع
بنسبة 1 إلى 20 فهو التركيز الأمثل لقتل الجراثيم. معظم الخدمات الطبية يستخدمون
تركيز 1 إلى 20 لاختبار الحساسية بيد أن خواص الحركية الدوائية لهذه التركيبة من
الصعب تحديدها لتقرير الجرعة وبرنامج الإعطاء للوصول لنسبة 1 إلى 20 في موقع
الإصابة في الجسم. وبالرغم من عبور هذه التركيبة عبور الحاجز (دم- بروستات) فمركبات
السلفا تكون غير فعالة في الأوساط الصديدية لتوفر مادة حمض بارا أمينوبينزويك بشكل
حر المنطلق من العدلات الميتة. المشاركة بين السلفاميدات والتريميثوبريم ذات تأثير
متآزر قاتل لجراثيم المكورات العنقودية والعقدية والاي كولاي والبروتيوس. ويختلف
تاثير هذا المشاركة على الكليبسيلا والمكورات المعوية، أما الزوائف فهي مقاومة
لها. تتعلق بهذه المشاركة العديد من التاثيرات الجانبية، والجرعة المنخفضة طويلة
الأمد قد تقود إلى تثبيط عمل نقي العظم التهاب القرنية والملتحمة سيكا (العين
الجافة) عند الكلاب.
Dosage Regimens for UTI:
برامج
الجرعات في التهاب المجاري البولية:
Currently,
the duration of therapy for UTI is controversial. Although animals are
routinely treated with antimicrobial drugs for 10–14 days, shorter duration
antimicrobial regimens are routinely prescribed in human patients, including
single-dose fluoroquinolone therapy. A clinical comparison of 3 days of therapy
with a once-daily high dose of enrofloxacin with 2 wk of twice daily
amoxicillin-clavulanic acid showed equivalence in the treatment of simple UTI
in dogs. However, further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage
regimens for different classes of antimicrobials, and it is inappropriate to
use fluoroquinolones as first-line therapy for simple UTIs. Animals with
complicated UTI may require longer courses of therapy, and underlying pathology
must be addressed. Chronic complicated cases of UTI, pyelonephritis, and
prostatitis may require antimicrobial treatment for 4–6 wk, with the risk of
selecting for antimicrobial resistance. A follow-up urine culture should be
performed after 4–7 days of therapy to determine efficacy. If the same or a
different pathogen is seen, then an alternative therapy should be chosen and
the culture repeated again after 4–7 days. Urine should also be cultured 7–10
days after completing antimicrobial therapy to determine whether the UTI has
resolved or recurred.
المدة العلاجية لالتهاب المجاري
البولية في هذه الأيام أمر مثير للجدل. وعلى الرغم من ذلك فالحيوانات تعالج بشكل
روتيني بالمضادات الحيوية ما بين 10 - 14 يوماً، وبرامج علاجية أقصر عند البشر
يمكن أن توصف لعلاج نفس الحالة بما فيها الجرعة الأحادية من الفلوروكينولون.
فالمقارنة العلاجية ذات 3 أيام بجرعة واحدة عالية من الإنروفلوكساسين مع جرعة أسبوعين
مرتين يومياً للاموكسيسلين مع الكلافولانيك أسيد نجد أن النتائج متقاربة في علاج
الاتهابات البولية البسيطة عند الكلاب. مع أن الدراسات الموسعة مطلوبة أيضاً
لتحديد برنامج الجرعات الأنسب لمختلف أنواع المضادات الحيوية أو عدم ملاءمتها
بالاعتماد على الفلوروكينولونات باعتبارها في المرتبة الاولى لعلاج التهابات
المجاري البولية البسيطة. قد تحتاج الحيوانات التي لديها التهابات بولية معقدة إلى
برامج علاجية أطول والمسببات المرضية الكامنة يجب أن يتم الكشف عنها أيضاً.
الالتهابات البولية المزمنة والتهاب الكلية والحويضة والتهاب البروستات قد تحتاج
علاجات من المضادات الحيوية التي تمتد ما بين 4 - 6 أسابيع، مع محاذير اختيار
المضادات الحيوية المقاومة. ويجب إجراء متابعة إجراء زرع بولي بعد 4 - 7 أيام.
ويجب أن يتم زراعة البول بعد 7 - 10 أيام من إتمام العلاج بالمضادات الحيوية
لتقرير ما إذا كان التهاب المجاري البولية قد تمت السيطرة عليه أو قد تم تأمينه.
Managing Multiple Episodes of UTI:
التعامل مع
مختلف أنماط التهاب المجاري البولية:
In
dogs and cats, if UTI occurs only once or twice yearly, each episode may be
treated as an acute, uncomplicated UTI. If episodes occur more often, and
predisposing causes of UTI cannot be identified or corrected, chronic low-dose therapy
may be necessary. Low antimicrobial concentrations in the urine may interfere
with fimbriae production by some pathogens and prevent their adhesion to the
uroepithelium. In dogs, recurrent UTIs are due to a different strain or species
of bacteria ~80% of the time; therefore, antimicrobial culture and
susceptibility is still indicated. Antimicrobial therapy should be started as
previously described and when urine culture is negative, continued daily at ⅓
the total daily dose. The antimicrobial should be administered last thing at
night to ensure that the bladder contains urine with a high antimicrobial
concentration for as long as possible.
إذا حدث التهاب المجاري البولية عند
الكلاب والقطط مرة أو مرتين سنوياً فإن كل نمط يجب أن يعالج على أنه التهاب بوليّ
حاد وغير معقد. أما إذا تكرر النمط أكثر من ذلك مع عدم إمكان تمييز العومل المهيئة
له أو حتى تصحيحها، فقد يكون العلاج بجرعات منخفضة من المضادات الحيوية طويلة
الأمد مطلوبة وضرورية. تراكيز المضادات الحيوية المنخفضة في البول يمكن أن تتدخل
في عملية تشكل خيوط الأهداب لبعض المسببات المرضية مانعة إياها من الالتصاق على
ظهارة المجاري البولية. قد يكون التهاب المجاري البولية المتكرر عند الكلاب متسبباً
عن مختلف عترات الجراثيم المختلفة قد يصل إلى 80% من الوقت، لذلك يجب أن تجرى
عملية الزرع الجرثومي واختبار الحساسية. ويجب أن تبدأ المعالجة الجرثومية قبل أن
تظهر النتائج وتكرر يومياً بثلث مقدار الجرعة المخصصة لهذا العقار. يجب أن يكون
آخر ما يقدم مساء هو عقار المضاد الحيوي لضمان احتواء المثانة على البول الحاوي
على نسبة عالية من المضاد الحيوي وبأطول فترة ممكنة.
Appropriate
antimicrobials for chronic, low-dose therapy include amoxicillin, ampicillin,
amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, doxycycline, cephalexin, cefadroxil, and
nitrofurantoin. A trimethoprim-sulfonamide can be used, but folate
supplementation should be provided (15 mg/kg, bid) to prevent bone marrow
suppression; there is also the risk of keratoconjunctivitis sicca developing
with longterm use. Although attractive for owner convenience, third-generation
cephalosporins such as cefpodoxime and cefovecin and fluoroquinolones should
not be used for longterm therapy. During longterm therapy, urine culture should
be repeated every 4–6 wk. As long as the culture is negative, therapy is
continued for 6 mo. If bacteriuria occurs, the infection is treated as an acute
episode with an appropriate antimicrobial. After 6 mo of bacteria-free urine,
the longterm, low-dose antimicrobial therapy may be discontinued, and many
animals will not have additional recurrences. In some cases, longterm therapy
may be continued for years in animals that continue to have recurrent UTIs.
أفضل المضادات الحيوية للاستخدام
للعلاج طويل الأمد وبجرعات منخفضة تتضمن الأموكسيسلين والأمبيسلين والأموكسيسلين
مع الكلافولينيك أسيد والدوكسيسيكلين والسيفاليكسين والسيفادروكسيل
والنيتروفيوران. ويمكن استخدام التريميثوبريم والسلفاميدات ولكن يجب التزويد
بمركبات الفولات بجرعة (15مغ/كغ مرتين يومياً) لمنع حدوث تثبيط نقي العظم، وهناك
خطورة حدوث حالة العين الجافة في حال الاستخدام المديد لهذا العلاج. وبالرغم من
ميل المالكين لاستخدام الجيل الثالث من السيفالوسبورينات مثل السيفادروكسيم
والسيفوفوسين والفلوروكينولونات فإنها لا يجب ان تستخدم للعلاج المديد. يجب إجراء
زرع البول في العلاجات طويلة الأمد ويكرر كل 4-6 أسابيع. وطالما بقيت نتائج الزرع
سلبية فالعلاج يجب ان يستمر لمدة 6 أشهر. وبعد 6 أشهر من بول خال من الجراثيم فإن
العلاج طويل الأمد قليل الجرعة يمكن أن يوقف وقد لا تحتاج هذه الحيوانات إعادة
العلاج مرة أخرى. في بعض الحلات قد يستمر لمدة أعوام عند الحيوانات التي تعاني من
التهابات المجاري البولية المتكررة.
Therapeutic Failures:
الفشل
العلاجي:
Treatment
failures may be due to poor owner compliance, inappropriate choice of
antimicrobials, inappropriate dose or duration of treatment, antimicrobial
resistance, superinfection, or an underlying predisposing cause (eg,
urolithiasis, neoplasia, urachal diverticula). If treatment for a simple or
complicated UTI fails, a thorough evaluation should be performed to determine
and, when possible, address the cause of failure. When faced with a therapeutic
failure, the practitioner must consider whether the UTI is due to a relapse or
a reinfection. Relapses due to infection by uropathogens with enhanced
intrinsic virulence occur with what should be effective antimicrobial therapy.
Strains of uropathogenic E coli have a number of virulence mechanisms
that enable them to invade, survive, and multiply within the uroepithelium. The
sequestration of uropathogenic E coli within the bladder uroepithelium
presents a great therapeutic challenge in both human and veterinary patients.
There is no clear consensus in the human medical literature about how to
approach these recurrent and persistent UTIs.
قد يكون فشل العلاج بسبب ضعف التزام
مالك أو الاختيار غير الملائم للمضاد الحيوي أو الفترات بين الجرعات غير ملائمة أو
وجود مقاومة للمضاد الحيوي أو عدوى ضاري
أو مسببات مهيئة كامنة (مثل الحصيات البولية التورمات أو رتوج ريشال). إذا فشلت
معالجة التهاب المجاري البول البسيطة أو المعقدة يجب أن يجرى تقييما مباشرا لتحديد
وإن أمكن تمييز السبب المباشر لهذا الفشل. وعند مواجهة المعالج حالة فشل علاج
فعليه أن يحدد ما إذا كان الأمر عبارة عن إنتاكس أم أنه إعادة العدوى. قد تكون
الانتكاسة نتيجة للمسببات المتواجدة في السبيل البولي مع تعزيز الفوعة الذاتية
التي تحدث مع ما يجب استخدامه من مضادات جرثومية فعالة. عترات الاي كولاي البولية
لديها عدة آليات خبيثة تمكنها من الغزو والبقاء على قيد الحياة والتكاثر ضمن
الطبقة الظهارية للسبيل البولي. فبقاء الاي كولاي المسببة للعدوى حبيسة الطبقة
الظهارية للمثانة يشكل تحديا علاجيا كبيرا عند كل من الانسان والحيوان. ولا يوجد
إجماع واضح في الثقافة الطبية حول الطريقة المثلى للتعامل مع مثل هذه العدوى
المتكررة من التهاب المجاري البولية.
Antimicrobial Resistance in Uropathogens:
مقاومة
المضادات الجرثومية بالنسبة للمسببات المرضية البولية:
Acquired
resistance to antimicrobials by uropathogens is of great concern in both human
and veterinary medicine. The prevalence of multidrug resistance in uropathogens
is increasing, particularly in infections in dogs and cats. Extended-spectrum
β-lactamase genes are increasingly identified in E coli isolates from
companion animals. Increases in the occurrence of fluoroquionolone-resistant E
coli in dogs have been widely reported. Because the mechanism of resistance
to fluoroquinolones frequently involves efflux pumps, it also conveys multidrug
resistance. Fluoroquinolone resistance is also increasing in other
uropathogens, including enterococci, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus
pseudintermedius isolates. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci have been
identified in cases of canine UTI. There is increasing evidence that animals
are an important reservoir of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria causing
infections in people. Enterococci isolated from canine UTIs have been
associated with several different resistant phenotypes, with most exhibiting
resistance to three or more antimicrobials.
المناعة التي تكتسبها المسببات
المرضية البولية هي مصدر اهتمام بالغ عند كل من الطب البشري والبيطري. فالمقاومة
المتفشية للمسببات المرضية البولية ضد المضادات الجرثومية المتعددة تزداد. وخاصة عند
إصابة الكلاب والقطط. الجين المقاوم للبيتالاكتام عند الجراثيم يزداد تمددا وخاصة
عند الاي كولاي المعزولة من الحيوانات المدللة. وقد تم الابلاغ بشكل واسع عن حدوث
زيادة في مقاومة مركبات الفلوروكينولونات لدى الاي كولاي عند الكلاب. وبما أن آلية
المقاومة للفلوروكينولونات تتعلق باستمرار بمضخات ايفلوكس فقد تنتقل تلك المقاومة
لتصبح مقاومة لمختلف المضادات البكتيرية. كما تزداد مقاومة الفلوروكينولونات عند
باقي المسببات الجرثومية للالتهابات البولية بما في ذلك عزولات المكورات المعوية
والبروتيوس ميرابيلي، والمكورات العنقودية بسيدو إنترميديوس، وعزلت المكورات
العنقودية المقاومة للميثيسلينات من الكلاب المصابة بالتهاب المجاري البولية. هناك
أدلة متزايدة عن كون الحيوانات عبارة عن خزانات للجراثيم المقاومة للمضادات
الحيوية التي يمكن أن تنتقل إلى البشر لاحقا. المكورات المعوية المعزولة من
التهابات البول عند الكلاب اثبت تعلقها بمختلف مظاهر المقاومة للمضادات، مع تزايد
إبدائها للمقاومة ضد ثلاثة أو أكثر من المضادات الجرثومية.
One
Enterococcus faecium isolate displayed high-level resistance to
vancomycin and gentamicin. Sequence analysis suggested that resistance was due
to gene exchange between human and canine enterococci. The use of “last resort”
human antimicrobials in veterinary patients with resistant infections is
controversial. Vancomycin, imipenem-cilastatin, meropenem, fosfomycin,
quinupristin-dalfopristin, and tigecycline should not be used routinely in
treatment of UTI in animals. Nonantimicrobial control of infection should be
considered whenever feasible. Custom-made vaccines, cranberry juice/extract,
probiotics and adherence/colonization inhibitors, and establishment of
asymptomatic bacteriuria may help preserve the efficacy of antimicrobials.
أبدت عزلة واحدة من المكورة المعوية فاسيوم مستوى عال للمقاومة ضد
الفانكومايسين والجنتاميسين. وافترض التحليل المتكرر أن هذه المقاومة قد تعود إلى
التبادل الجيني ما بين المكورات المعوية البشرية والكلبية. هنا يكون استعمال
المضادات الجرثومية البشرية هي "الملاذ الأخير" عند الحيوانات المصابة
وهذا الأمر هو شيء مثير للجدل. المضادات الحيوية (فانكومايسين،
إيميبينيم-سيلاستاتين، ميروبينيم، فوسفومايسين، كوينبريستين-دالفوبريستين،
والديكاسيكلين) يجب أن لا تستعمل بشكل روتيني لعلاج الالتهابات البولية عند الحيوانات.
يجب الاعتماد على التحكم بالعدوى غير المستخدم للمضادات الجرثومية يجب أن يقرر
كلما أمكن ذلك. فاللقاحات المصنوعة محليا، عصير التوت البري ومستخلصه، مركبات
البروبيوتيك، ومقاومات الالتصاق والغزو وتحفيز بيلة جرثومية عديمة الأعراض قد
تمكننا من ادخار فعالية المضادات الجرثومية.